⚡🔋How energy moves through systems is a fundamental part of physics — and an important concept in electrical, mechanical, and thermal applications. If you’re analyzing a circuit, a moving object, or heat transfer, knowing how to calculate energy transferred helps you quantify how much work is being done.
In this article, we’ll explain the formulas, give real-life examples, and provide a calculator to make things easier.
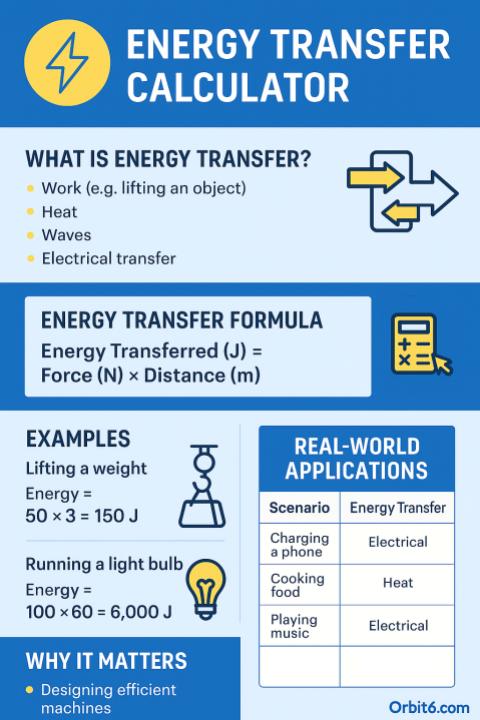
🙋 What Is Energy Transferred?
Energy transferred is the amount of energy moved from one system, object, or place to another. It can happen in many forms:
- Electrical (e.g., energy used by a light bulb)
- Mechanical (e.g., moving an object)
- Thermal (e.g., heating water)
Energy is measured in joules (J).
📚 Formula for Energy Transferred
There are several ways to calculate energy transferred depending on the context:
1. Electrical Energy
If you’re dealing with electricity, use:
Energy (J) = Power (W) × Time (s)Where:
- Power is in watts (W)
- Time is in seconds (s)
2. Mechanical Work
If a force is applied to move an object:
Energy (J) = Force (N) × Distance (m)Where:
- Force is in newtons (N)
- Distance is in meters (m)
3. Heat Transfer
If heating or cooling is involved:
Energy (J) = Mass (kg) × Specific Heat (J/kg°C) × Temperature Change (°C)For this article, we’ll focus on the electrical energy transfer formula.
💡 Example Calculation
You have a 60-watt light bulb running for 2 minutes. How much energy is transferred?
Convert time to seconds:2 minutes = 120 seconds
Now use the formula:Energy = 60 W × 120 s = 7,200 J
So, 7,200 joules of energy are transferred.
📌 Final Thoughts
Knowing how to calculate energy transferred allows you to quantify how much energy is being used or moved in systems — from simple appliances to complex engineering problems. Use the calculator above to simplify your work and better understand energy flow.